Evaluación del rendimiento y escalabilidad en redes SDN usando sFlow
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
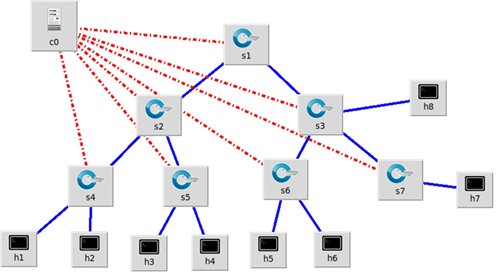
Las redes definidas por software (SDN) permiten separar el plano de datos del plano de control, permitiendo una gestión centralizada y flexible de la red. Las redes tradicionales enfrentan grandes desafíos relacionados con la escalabilidad y la flexibilidad; por lo tanto, es necesario implementar técnicas de monitoreo eficiente del tráfico. Al implementar una herramienta como sFlow en la red SDN, se permite optimizar el rendimiento y la gestión de los recursos, permitiendo analizar la escalabilidad de la red. En este trabajo, se analiza la integración del protocolo sFlow en una arquitectura SDN con el objetivo de recolectar información en tiempo real sobre el estado de la red y analizar la escalabilidad. Se desarrolló una topología con el entorno de simulación Mininet y el controlador Ryu, implementando el protocolo sFlow y sFlow-RT para capturar métricas de tráfico como paquetes descartados, jitter, throughput, tráfico total. Los resultados obtenidos permiten analizar la escalabilidad de la red al aumentar el número de dispositivos. Al incrementar la cantidad de dispositivos, la capacidad de la red empieza a disminuir, especialmente a partir de tener más de treinta dispositivos conectados, lo que conduce a tener más pérdida de paquetes y fallas en la recepción. Este comportamiento depende mucho de la eficiencia en la gestión del controlador.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.displayStats.downloads##
Detalles del artículo
Sección

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución 4.0.
Los autores que publican en esta revista están de acuerdo con los siguientes términos: Los autores conservan los derechos de autor y garantizan a la revista el derecho de ser la primera publicación del trabajo al igual que licenciado bajo una Creative Commons Attribution License que permite a otros compartir el trabajo con un reconocimiento de la autoría del trabajo y la publicación inicial en esta revista. Los autores pueden establecer por separado acuerdos adicionales para la distribución no exclusiva de la versión de la obra publicada en la revista (por ejemplo, situarlo en un repositorio institucional o publicarlo en un libro), con un reconocimiento de su publicación inicial en esta revista. Se permite y se anima a los autores a difundir sus trabajos electrónicamente (por ejemplo, en repositorios institucionales o en su propio sitio web) antes y durante el proceso de envío, ya que puede dar lugar a intercambios productivos, así como a una citación más temprana y mayor de los trabajos publicados.Cómo citar
Referencias
[1] A. M. D. Tello and M. Abolhasan, “Sdn controllers scalability and performance study,” in the 13th International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Systems (ICSPCS), 2019, pp. 1–10.
[2] M. Wang, Y. Lu, and J. Qin, “Source-based defense against ddos attacks in sdn based on sflow and som,” IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 2097–2116, 2022.
[3] O. V. Peterson, Cascone and Davie, “Software-defined networks: A systems approach: Use cases,” https://sdn.systemsapproach.org/uses.html, 2022, accessed: 2025-07-02.
[4] O. D. Adeniji, “Scalable flow based management scheme in software define network (sdn) using sflow,” WSEAS Transactions on Computers, vol. 22, pp. 64–69, 2023.
[5] InMon Corp., “sflow-rt: Real-time network analytics engine,” https://sflow-rt.com/, 2025, accedido el 02 julio 2025.
[6] A. Ram, M. P. Dutta, and S. K. Chakraborty, “A flow-based performance evaluation on ryu sdn controller,” Journal of The Institution of Engineers (India): Series B, vol. 105, pp. 203–215, 2024.
[7] K. Benzekki, A. El Fergougui, and A. Elbelrhiti Elalaoui, “Software- defined networking (sdn): a survey,” Security and Communication Networks, vol. 9, no. 18, pp. 5803–5833, 2016. [Online]. Available: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/sec.1737
[8] M. A. Diouf, S. Ouya, J. Klein, and T. F. Bissyande´, “Software security in software-defined networking: A systematic literature review,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.13828, 2025.
[9] Z. Latif, K. Sharif, F. Li, M. M. Karim, S. Biswas, and Y. Wang, “A comprehensive survey of interface protocols for software defined networks,” Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 156, p. 102563, 2020.
[10] U. I. Sunday and S. D. Akhibi, “Application of software-defined networking,” European Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 27–48, 2022.
[11] X. Liu, X. Zhang, Z. Li, Z. Zhang, and Z. Zhang, “Towards sflow and adaptive polling sampling for deep learning-based intrusion detection,” Future Generation Computer Systems, vol. 101, pp. 1–9, 2019.
[12] S. Hublikar, V. Eligar, and A. Kakhandki, “Detecting denial-of-service attacks using sflow,” in Inventive Communication and Computational Technologies, G. Ranganathan, J. Chen, and A. Rocha, Eds. Singapore: Springer Singapore, 2020, pp. 483–491.
[13] sFlow RT, “sflow-rt real-time analytics,” 2025, accedido: 27 de abril de 2025. [Online]. Available: https://sflow-rt.com
[14] M. Ilham and N. R. Rosyid, “Pengembangan aplikasi pemantauan ja- ringan berbasis web pada software-defined networking dengan protokol sflow,” Jurnal Teknologi Informasi dan Ilmu Komputer, vol. 8, no. 6, pp. 1117–1126, 2021.
[15] M. M. Elmoslemany, A. S. Tag Eldien, and M. M. Selim, “Performance analysis in software defined network (sdn) multi-controllers,” Delta University Scientific Journal, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 181–192, 2023.