Algoritmo adaptativo para consumo energético en redes de internet de las cosas
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
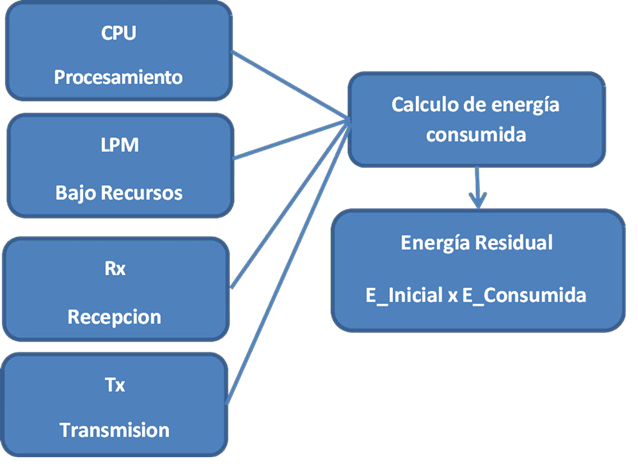
Este proyecto planteó el diseño e implementación de un algoritmo adaptativo para optimizar el consumo energético en redes de Internet de las Cosas (IoT) que utiliza el protocolo de enrutamiento RPL. La investigación respondió a la necesidad de mejorar la eficiencia de los dispositivos IoT que dependen de baterías limitadas, especialmente en contextos con infraestructura eléctrica limitada, como el cantón Mocache, Ecuador. Mediante la integración de métricas como la energía residual, la calidad de enlace (ETX) y la intensidad de señal (RSSI), el algoritmo permitió ajustar dinámicamente la potencia de transmisión y seleccionar rutas más eficientes, reduciendo las pérdidas de energía sin comprometer la calidad del servicio. La metodología se basó en simulaciones controladas en Cooja/Contiki-OS, con un escenario doméstico de tres nodos (coordinador, sensor y actuador), y se ejecutaron dos tratamientos: RPL estándar y RPL modificado con el algoritmo propuesto. Los resultados demostraron una reducción del 22% en el consumo energético promedio (de 35 mJ a 27 mJ por nodo), un incremento del PDR del 94.5% al 95.2% y una disminución de los cambios de padre, lo que evidencia una mayor estabilidad del DODAG. La propuesta alcanza una eficiencia comparable a la de trabajos previos, manteniendo una sobrecarga computacional baja y operando en microcontroladores con recursos limitados. Se concluye que el algoritmo adaptativo representa una solución viable para redes IoT domésticas y rurales con limitaciones energéticas, aportando un equilibrio entre el ahorro energético y la simplicidad de implementación.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.displayStats.downloads##
Detalles del artículo
Sección

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución 4.0.
Los autores que publican en esta revista están de acuerdo con los siguientes términos: Los autores conservan los derechos de autor y garantizan a la revista el derecho de ser la primera publicación del trabajo al igual que licenciado bajo una Creative Commons Attribution License que permite a otros compartir el trabajo con un reconocimiento de la autoría del trabajo y la publicación inicial en esta revista. Los autores pueden establecer por separado acuerdos adicionales para la distribución no exclusiva de la versión de la obra publicada en la revista (por ejemplo, situarlo en un repositorio institucional o publicarlo en un libro), con un reconocimiento de su publicación inicial en esta revista. Se permite y se anima a los autores a difundir sus trabajos electrónicamente (por ejemplo, en repositorios institucionales o en su propio sitio web) antes y durante el proceso de envío, ya que puede dar lugar a intercambios productivos, así como a una citación más temprana y mayor de los trabajos publicados.Cómo citar
Referencias
[1] K. Elgazzar et al., “Revisiting the Internet of Things: New Trends, Opportunities and Grand Challenges,” Frontiers in the Internet of Things, vol. 1, Nov. 2022, doi: 10.3389/friot.2022.1073780.
[2] J. Sebastián and T. Daza, “Routing IOT,” Jul. 29, 2022, Universidad de los Andes, Bogotá. Accessed: Oct. 04, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://hdl.handle.net/1992/59452
[3] T. V Manohar and Dr. T. Dharini, “Energy Efficiency in IoT: Challenges, Techniques, and Future Directions,” International Journal of Innovative Research in Technology, vol. 11, no. 5, pp. 1136–1142, 2024, Accessed: Oct. 05, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://ijirt.org/article?manuscript=168552
[4] K. F. Haque, A. Abdelgawad, V. P. Yanambaka, and K. Yelamarthi, “An Energy-Efficient and Reliable RPL for IoT,” IEEE World Forum on Internet of Things, WF-IoT 2020 - Symposium Proceedings, Jun. 2020, doi: 10.1109/WF-IOT48130.2020.9221450.
[5] T. Winter et al., “RPL: IPv6 Routing Protocol for Low-Power and Lossy Networks,” Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), Mar. 2012, doi: 10.17487/rfc6550.
[6] R. Elsas, E. De Poorter, and J. Hoebeke, “DRiPLOF: An RPL Extension for Multi-Interface Wireless Sensor Networks in Interference-Prone Environments,” Sensors, vol. 22, no. 10, p. 3906, May 2022, doi: 10.3390/S22103906/S1.
[7] Z. A. Almusaylim, N. Z. Jhanjhi, and A. Alhumam, “Detection and Mitigation of RPL Rank and Version Number Attacks in the Internet of Things: SRPL-RP,” Sensors, vol. 20, no. 21, p. 5997, Nov. 2020, doi: 10.3390/S20215997.
[8] S. Sennan, S. Ramasubbareddy, A. K. Luhach, A. Nayyar, and B. Qureshi, “CT-RPL: Cluster Tree Based Routing Protocol to Maximize the Lifetime of Internet of Things,” Sensors, Vol. 20, Page 5858, vol. 20, no. 20, p. 5858, Oct. 2020, doi: 10.3390/S20205858.
[9] S. Quevedo, A. B. Carrasco, K. J. L. Cabrera, C. E. S. Parrales, and V. B. S. Soledispa, “Análisis del impacto de los apagones de energía eléctrica en la rentabilidad de las grandes empresas en la provincia del Guayas, 2024,” Polo del Conocimiento, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 1411–1430, May 2025, doi: 10.23857/pc.v10i5.9513.
[10] Z. Shelby, K. Hartke, and C. Bormann, “The Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP),” Internet Engineering Task Force, Jun. 2020, Accessed: Oct. 04, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc7252
[11] S. Ibrahimy, H. Lamaazi, and N. Benamar, “IoT Nodes Behavior Analysis Under Constrained Environment Using RPL Protocol,” 2021 3rd IEEE Middle East and North Africa COMMunications Conference, MENACOMM 2021, pp. 74–79, 2021, doi: 10.1109/MENACOMM50742.2021.9678215.
[12] S. Sennan, S. Ramasubbareddy, A. Nayyar, Y. Nam, and M. Abouhawwash, “LOA-RPL: Novel Energy-Efficient Routing Protocol for the Internet of Things Using Lion Optimization Algorithm to Maximize Network Lifetime,” Computers, Materials and Continua, vol. 69, no. 1, pp. 351–371, May 2021, doi: 10.32604/CMC.2021.017360.
[13] M. Tarif, M. Homaei, A. Mirzaei, and B. Nouri-Moghaddam, “Optimizing RPL Routing Using Tabu Search to Improve Link Stability and Energy Consumption in IoT Networks,” Aug. 2024, Accessed: Oct. 04, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2408.06702
[14] S. Srividhya, S. Sankaranarayanan, S. A. Kozlov, and J. J. P. C. Rodrigues, “Fuzzy Aggregator Based Energy Aware RPL Routing for IoT Enabled Forest Environment,” Computers, Materials & Continua, vol. 72, no. 2, pp. 4039–4055, Mar. 2022, doi: 10.32604/CMC.2022.026306.
[15] Y. Wang, Y. Li, J. Lei, and F. Shang, “Robust and energy-efficient RPL optimization algorithm with scalable deep reinforcement learning for IIoT,” Computer Networks, vol. 255, p. 110894, Dec. 2024, doi: 10.1016/J.COMNET.2024.110894.
[16] M. R. Poornima, H. S. Vimala, and J. Shreyas, “Fuzzy-Based Novel Cross-Layer RPL Objective Function for Energy-Aware Routing in IoT,” International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 1–25, Dec. 2025, doi: 10.1007/S44196-025-00916-2/FIGURES/21.
[17] R. Sirwan and M. Al-Ani, “Adaptive Routing Protocol RPL in IOT Networks based on Content Centric,” Jun. 2020, Accessed: Oct. 04, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343837257_Adaptive_Routing_Protocol_RPL_in_IOT_Networks_based_on_Content_Centric