Design and simulation of circularly polarized, quasi-square microstrip antennas for microsatellites: A practical guide to simulation with HFSS™ software
Main Article Content
Abstract
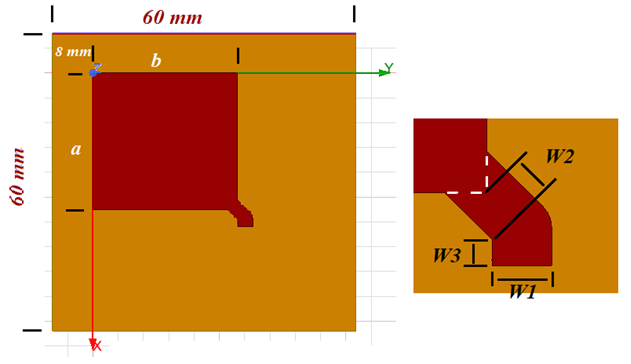
This paper presents a practical guide for the design of a Right-Hand Circular Polarization (RHCP) microstrip antenna using HFSS software. The design considers an antenna to acquire information transmitted by the Global Positioning System (GPS) in the L1 band. This signal is used by the Attitude Control Unit (ACU) to improve the positioning control of a microsatellite traveling in a Low Earth Orbit (LEO). Following the proposed procedure, values of an Axial Ratio (AR) of 1.22 dB, a directivity of 5.14 dB in the broadside direction, and an AR bandwidth of 15 MHz were obtained.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms: Authors retain the copyright and guarantee the journal the right to be the first publication of the work, as well as, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others share the work with an acknowledgment of the authorship of the work and the initial publication in this journal. Authors may separately establish additional agreements for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published in the journal (for example, placing it in an institutional repository or publishing it in a book), with acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal. Authors are allowed and encouraged to disseminate their work electronically (for example, in institutional repositories or on their own website) before and during the submission process, as it may lead to productive exchanges as well as further citation earliest and oldest of published works.
How to Cite
References
[1] A. Cratere, L. Gagliardi, G. A. Sanca, F. Golmar, y F. Dell’Olio, “On-Board Computer for CubeSats: State-of-the-Art and Future Trends”, IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 99537–99569, 2024, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3428388.
[2] J. P. Tovar Soto, C. F. Pareja Figueredo, J. S. Vargas Cañón, y L. C. Gutiérrez Martínez, “A review of the current state of Pico and Nanosatellites: some applications in Latin America and other regions of the world”, GRAINE. Boletín de Investigaciones., vol. 2, no 1, pp. 13–30, sep. 2020, doi: 10.52408/gbdivol2iss1pp13-30.
[3] A. Zeedan y T. Khattab, “CubeSat Communication Subsystems: A Review of On-Board Transceiver Architectures, Protocols, and Performance”, IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 88161–88183, 2023, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3304419.
[4] S. Malisuwan y B. Kanchanarat, “Small Satellites for Low-Cost Space Access: Launch, Deployment, Integration, and In-Space Logistics”, American Journal of Industrial and Business Management, vol. 12, no 10, pp. 1480–1497, 2022, doi: 10.4236/ajibm.2022.1210082.
[5] K. S. Low, M. S. C. Tissera, y J. W. Chia, “In-orbit results of VELOX-II nanosatellite”, en 2016 IEEE Region 10 Conference (TENCON), IEEE, nov. 2016, pp. 3658–3663. doi: 10.1109/TENCON.2016.7848740.
[6] S. A. Ali Shah y U. Arshad, “General system design of Cubesat in LEO for IR imaging”, en 2013 International Conference on Aerospace Science & Engineering (ICASE), IEEE, ago. 2013, pp. 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICASE.2013.6785552.
[7] J. Li, M. Post, T. Wright, y R. Lee, “Design of Attitude Control Systems for CubeSat-Class Nanosatellite”, Journal of Control Science and Engineering, vol. 2013, pp. 1–15, 2013, doi: 10.1155/2013/657182.
[8] N. Nadarajah, P. J. G. Teunissen, y P. J. Buist, “Attitude determination of LEO satellites using an array of GNSS sensors”, en 2012 15th International Conference on Information Fusion, Singapore: IEEE, jul. 2012, pp. 1066–1072.
[9] Ansoft Corporation, User’s guide – High Frequency Structure Simulator. Pittsburgh, PA: Ansoft Corporation, 2005.
[10] Rogers Corporation, “TMM® 10i Laminates”, https://www.rogerscorp.com/advanced-electronics-solutions/ tmm-laminates/tmm-10i-laminates.
[11] J. R. James y P. S. Hall, Handbook of Microstrip Antennas, 2a ed. London - UK: Peter Peregrinus Ltd., 1989.
[12] W. Richards, Yuen Lo, y D. Harrison, “An improved theory for microstrip antennas and applications”, IEEE Trans Antennas Propag, vol. 29, no 1, pp. 38–46, ene. 1981, doi: 10.1109/TAP.1981.1142524.
[13] R. Bancroft, Microstrip and printed antenna design, 2th ed. Raleigh, NC: SciTech publishing Inc., 2009.
[14] D. Chagas y J. C. da S. Lacav, “Design of Low-Cost Probe-Fed Microstrip Antennas”, en Microstrip Antennas, InTech, 2011. doi: 10.5772/14523.
[15] A. F. Tinoco S, D. C. Nascimento, y J. C. da S. Lacava, “Rectangular microstrip antenna design suitable for undergraduate courses”, en 2008 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, IEEE, jul. 2008, pp. 1–4. doi: 10.1109/APS.2008.4619275.