Prototipo de sistema automatizado de riego mejora el rendimiento de la papa (Solanum tuberosum L.) en Riobamba-Ecuador usando sensores de redes inalámbricos-WSN y 6LoWPAN
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
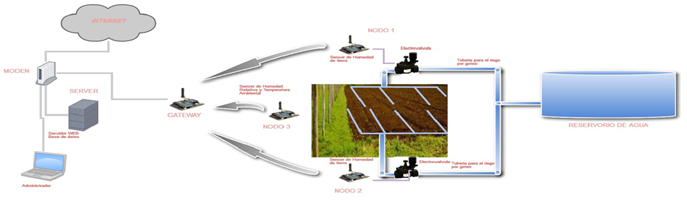
El objetivo de esta investigación fue optimizar el agua de riego en el cultivo de la papa (Solanum tuberosum L. cv. INIAP Natividad) para asegurar la máxima productividad del cultivo, utilizando WSN de acuerdo a las condiciones agroecológicas de la zona, lo cual permitió monitorear parámetros ambientales en el cultivo de la papa y asegurar un sistema de control eficiente en el riego. Se implementó la red WSN utilizando cuatro módulos Arduino configurados con 6LoWPAN, dos módulos controlaron las electroválvulas conjuntamente con sensores FC-28 que captan la humedad del suelo, y a través del sensor DHT11 la temperatura ambiental y la humedad relativa. El cuarto módulo funcionó como Gateway a través del cual se envía información hacia una base de datos desarrollado en PostgreSQL. Adicionalmente, se configuró un servidor Web (Apache) para visualizar el control del sistema de riego por goteo desarrollado en php, JAVA. Se definió T1 = riego automatizado, evidencia con una mayor productividad en el cultivo de la papa en un 19,2%, con un consumo de agua del 20% menos que el T2 (riego manual). Esto evidencia un claro ahorro del recurso hídrico y un óptimo desarrollo en el cultivo de la papa al compararlo con el sistema tradicional.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.displayStats.downloads##
Detalles del artículo
Número
Sección

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución 4.0.
Los autores que publican en esta revista están de acuerdo con los siguientes términos: Los autores conservan los derechos de autor y garantizan a la revista el derecho de ser la primera publicación del trabajo al igual que licenciado bajo una Creative Commons Attribution License que permite a otros compartir el trabajo con un reconocimiento de la autoría del trabajo y la publicación inicial en esta revista. Los autores pueden establecer por separado acuerdos adicionales para la distribución no exclusiva de la versión de la obra publicada en la revista (por ejemplo, situarlo en un repositorio institucional o publicarlo en un libro), con un reconocimiento de su publicación inicial en esta revista. Se permite y se anima a los autores a difundir sus trabajos electrónicamente (por ejemplo, en repositorios institucionales o en su propio sitio web) antes y durante el proceso de envío, ya que puede dar lugar a intercambios productivos, así como a una citación más temprana y mayor de los trabajos publicados.