Análisis del desempeño de los esquemas de modulación BPSK y QPSK para diferentes condiciones de canales en sistema GFDM
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
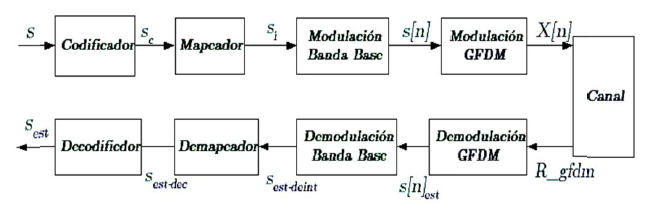
Hoy en día, las redes de comunicación inalámbricas han aumentado sustancialmente el número de información de transmisión. Por lo tanto, es necesario el desarrollo de nuevas tecnologías que satisfagan esta demanda en los mercados. En este contexto, la Multiplexación por División de Frecuencia Generalizada (GFDM) surge como una solución para las redes de comunicación inalámbricas futuras. El objetivo principal de esta investigación es analizar el desempeño de la modulación de BPSK y QPSK para diferentes condiciones del canal de comunicación en el sistema GFDM. Se presentan las modulaciones BPSK, QPSK y el modelo de señal de matriz del sistema GFDM. El desempeño se evalúa en términos de tasa de errores de bits (BER) y se implementan tres canales diferentes: ideal, fijo y fijo aleatorio. Los resultados de la simulación de detección representan las curvas de desempeño para diferentes escenarios y modulaciones. Se puede observar que, para todos los canales, la modulación BPSK supera a la modulación QPSK.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.displayStats.downloads##
Detalles del artículo
Número
Sección

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución 4.0.
Los autores que publican en esta revista están de acuerdo con los siguientes términos: Los autores conservan los derechos de autor y garantizan a la revista el derecho de ser la primera publicación del trabajo al igual que licenciado bajo una Creative Commons Attribution License que permite a otros compartir el trabajo con un reconocimiento de la autoría del trabajo y la publicación inicial en esta revista. Los autores pueden establecer por separado acuerdos adicionales para la distribución no exclusiva de la versión de la obra publicada en la revista (por ejemplo, situarlo en un repositorio institucional o publicarlo en un libro), con un reconocimiento de su publicación inicial en esta revista. Se permite y se anima a los autores a difundir sus trabajos electrónicamente (por ejemplo, en repositorios institucionales o en su propio sitio web) antes y durante el proceso de envío, ya que puede dar lugar a intercambios productivos, así como a una citación más temprana y mayor de los trabajos publicados.