Design of an interactive application for digital terrestrial television based on Ginga Middleware for marketing online products
Main Article Content
Abstract
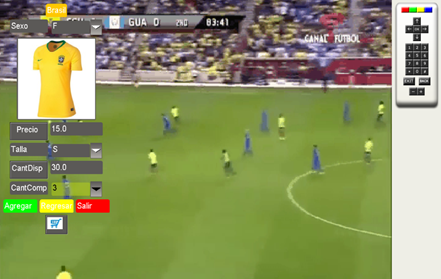
The introduction of digital terrestrial television (DTT) brings multiple advantages. On the one hand, there are those advantages that allow optimizing the use of the radioelectric spectrum, such as (i) the possibility of transmitting in adjacent channels, (ii) transmission of multiple contents through the same radio channel, and (iii) the use of single frequency networks (SFN). On the other hand, another advantage, not fully exploited, is to offer interactive content and value-added services, such as learning (T-Learning), voting (T‑Voting), commerce (T-Commerce), etc. In ISDB-Tb interactivity, using the GINGA middleware developed in Brazil is possible. In Ecuador, ISDB-Tb was adopted as a DTT standard in 2010. Nowadays, and despite having passed several years, the implementation of ISDB-Tb in Ecuador is still in its early stages. Therefore, none of its most important features has yet been exploited. This article presents the design of an interactive application that allows products to be commercialized through DTT. The application design was developed in Ginga-J to allow security options. In addition, the company's database was created in MySQL with an APACHE server. The application enables the user to pay by credit card or by PAYPAL. Digital certificates and signatures were included to encode the information, protect the data, and verify the identity of both parties, making the purchase a safe process. Using digital signatures prevents the company from storing user financial data or making a fraudulent transaction, and vice versa. User acceptance tests (UAT) determined that the application is practical, the content is organized and understandable, and its handling is like purchasing online. Finally, the investment is verified with a discount on the balance of the user's account.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms: Authors retain the copyright and guarantee the journal the right to be the first publication of the work, as well as, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others share the work with an acknowledgment of the authorship of the work and the initial publication in this journal. Authors may separately establish additional agreements for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published in the journal (for example, placing it in an institutional repository or publishing it in a book), with acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal. Authors are allowed and encouraged to disseminate their work electronically (for example, in institutional repositories or on their own website) before and during the submission process, as it may lead to productive exchanges as well as further citation earliest and oldest of published works.
How to Cite
References
[2] C. Pérez Vega, Fundamentos de televisión analógica y digital (2a. ed.). Santander: Editorial de la Universidad de Cantabria, 2012.
[3] A. C. Paredes, N. M. Tonguino, G. F. Olmedo and F. R. Acosta, "Performance analysis on return channel for interactive digital TV ISDB-Tb system," in Proc. 2012 IEEE Latin-America Conference on Communications, Cuenca, 2012, pp. 1-4.
[4] Consejo Nacional de Telecomunicaciones de Ecuador, “Resolución N°. 084-05-CONATEL-2010. ” , Quito, Ecuador, Marzo 2010.
[5] J. Torres, “Diseño y desarrollo de una aplicación de contenidos interactivos para tv digital basada en el middleware ginga del sistema brasileño,” Grade thesis, ESPE, Quito, 2010.
[6] A. Morales, “Diseño de la red para interactividad en televisión digital terrestre e IPTV en el campus ESPE Sangolquí,” Grade thesis, ESPE, Quito, 2010.
[7] D. Martínez, " Estudio e investigación del MIDDLEWARE GINGA J del estándar brasileño de televisión digital. caso práctico: desarrollo de una aplicación interactiva aplicando metodología OPENUP /BASIC como parte del Proyecto ESPE-GINGA," Grade thesis, ESPE, Quito, Ecuador, 2011.
[8] D. Aulema, "Desarrollo de aplicaciones para TDT con GINGA-J," Maskay, vol. 2, Num 1, pp. 56-63, Nov. 2012.
[9] G. de Souza Filho, L. E. Cunha Leite, and C. E. Coelho Freire Batista, “No TitleGinga-J: The procedural middleware for the Brazilian digital TV system,” J. Brazilian Comput. Soc., vol. 13, pp. 47–56, 2007.
[10] D. Tavares, et. al., “Interactive Virtual Worlds in Brazilian Digital Television,” Workshop on Interactive Digital TV in Emergent Countries EuroITV, 2010.
[11] Soares, L.F.G., Rodrigues, R.F. y Moreno, M.F. Ginga-NCL: the declarative environment of the Brazilian digital TV System. J Braz Comp Soc 13, 37–46 (2007).
[12] Filho, G.L.d.S., Leite, L.E.C. y Batista, C.E.C.F. Ginga-J: The procedural middleware for the Brazilian digital TV system. J Braz Comp Soc 13, 47–56 (2007).
[13] J. Villanueva y C. Velásquez, “Informe Preliminar: Estado del Arte de Receptores Set-Top-Box – Aplicaciones,” Grade thesis, INICTEL – UNI, Lima, 2010.
[14] D. Williams, Pro PayPal E-Commerce. Apress, 2007.