Design and implement a Systems-on-Chip (MPSoC) multiprocessor interconnected by a Networks-on-Chip (NoC)
Main Article Content
Abstract
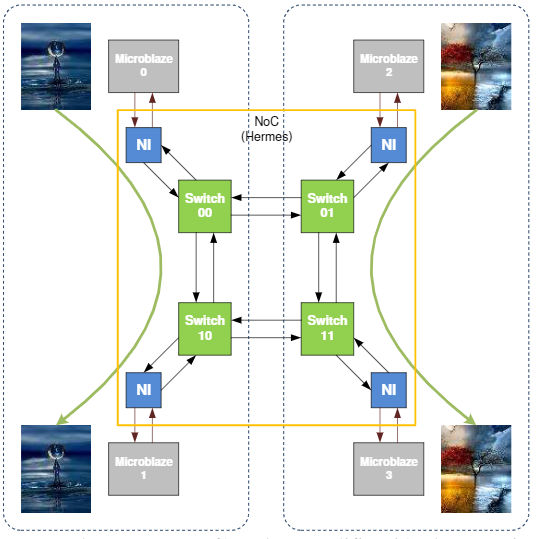
This document briefly characterizes the communication media used in multiprocessed architectures. The main objective of this characterization is to show a new communication model based on packet switching called Networks-On-Chip (NoC). This publication shows a network architecture called NoC Hermes, which was interconnected to a Multiprocessor-Systems-on-Chip (MPSoC) composed of four MicroBlaze processors. This connection was made thanks to the design and development of a Network Interface generated in VHDL code. The MicroBlaze processors could interact with the Hermes Switches through the Network Interface to create a multiprocessor architecture interconnected by a NoC. Another architecture of multiprocessors interconnected by buses was also created to make comparisons. A steganography application was developed for both architectures, in which two processors are multiprocessed and work simultaneously. Unfortunately, in this application, measuring the latency and energy consumption directly was impossible, so simulators were used to estimate these measurements.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms: Authors retain the copyright and guarantee the journal the right to be the first publication of the work, as well as, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others share the work with an acknowledgment of the authorship of the work and the initial publication in this journal. Authors may separately establish additional agreements for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published in the journal (for example, placing it in an institutional repository or publishing it in a book), with acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal. Authors are allowed and encouraged to disseminate their work electronically (for example, in institutional repositories or on their own website) before and during the submission process, as it may lead to productive exchanges as well as further citation earliest and oldest of published works.