Design and implementation of a QPSK demodulator using a central tendency technique
Main Article Content
Abstract
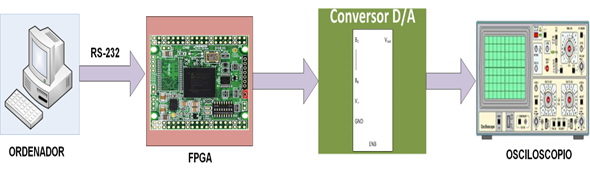
This paper describes a quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK) demodulator. The digital demodulator is based on the median for recovering data bits. The results showed that the median technique reduces complexity. The modulator consists of two different techniques: direct digital synthesis technique (DDS) and stored phases in read-only memories. These techniques were compared to probe the efficiency using parameters such as power consumption and the number of used elements. The modulator based on the memories is optimal. The modulator and demodulator were designed in VHDL language and were implemented in a Virtex-5 board from Xilinx.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms: Authors retain the copyright and guarantee the journal the right to be the first publication of the work, as well as, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others share the work with an acknowledgment of the authorship of the work and the initial publication in this journal. Authors may separately establish additional agreements for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published in the journal (for example, placing it in an institutional repository or publishing it in a book), with acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal. Authors are allowed and encouraged to disseminate their work electronically (for example, in institutional repositories or on their own website) before and during the submission process, as it may lead to productive exchanges as well as further citation earliest and oldest of published works.
How to Cite
References
[2] K. Feher, “FQPSK: A modulation-power efficient RF amplification proposal for increased spectral efficiency and capacity GMSK and 7rl4-QPSK compatible PHYstandard,” Doc. IEEE 802.11-93/97, July 1993.
[3] T. Pochiraju y V. Fusco, “Ultra-low power high bandwidth QPSK modulator,” in IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest, Atlanta, GA, USA, Jun. 2008, pp. 9-12.
[4] M R Raghavendra,“Design and development of high bit rate QPSK demodulator”, in IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Computing and Communication Technologies, Bangalore, India, Jan. 2013, pp. 1-5.
[5] T. Lee, H. R. B. Kennedy, R. A. Bodnar and W. Redman-White, “An MF Energy Harvesting Receiver with Slow QPSK Control Data Demodulator for Wide Area Low Duty Cycle Applications,” in IEEE 44th European Solid State Circuits Conference (ESSCIRC), Dresden, Germany, Sep. 2018, pp. 86-89.
[6] H. Takahashi, T. Kosugi, A. Hirata, K. Murata and N. Kukutsu, “10-Gbit/s QPSK modulator and demodulator for a 120-GHz-band wireless link,” in IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium, Anaheim, CA, USA, May 2010, pp. 632-635.
[7] D. Wagner, S. C. Kwatra and M. M. Jamali, “A single chip high data rate QPSK demodulator,” in IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Chicago, IL, USA, May 1993, pp. 2031-2034.
[8] A. Rai and V. N. Kumar, “Wideband acquisition technique for QPSK demodulator,” in IEEE International Conference on Recent Trends in Electronics, Information & Communication Technology (RTEICT), Bangalore, India, May 2016, pp. 490-493.
[9] W. Couch, Modern and Analog Communication Systems, Pearson, octava edición, 2012.
[10] K.Anitha, Umesharaddy y B.K.Sujatha, “FPGA Implementation of High Throughput Digital QPSK Modulator using Verilog HDL,” International Journal of Advanced Computer Research,vol. 4, 217 222, Mar. 2014.
[11] J. Gorgas, N. Cardiel, J. Zamorano, Estadística Básica para Estudiantes de Ciencias, Universidad Complutense de Madrid, España, Edición de Febrero 2011.
[12] XILINX, ISE In-Depth Tutorial, Mar, 2011.
G. van Rossum, El tutorial de Python, Sep. 2009.
[13] N. Solano, Implementación de un modulador y un demodulador QPSK en banda base, Escuela Politécnica Nacional, Ecuador, Febrero 2016. URL: http://bibdigital.epn.edu.ec/bitstream/15000/15229/1/CD-7004.pdf.