Performance of worm algorithms in the navigation of a mobile robotic platform
Main Article Content
Abstract
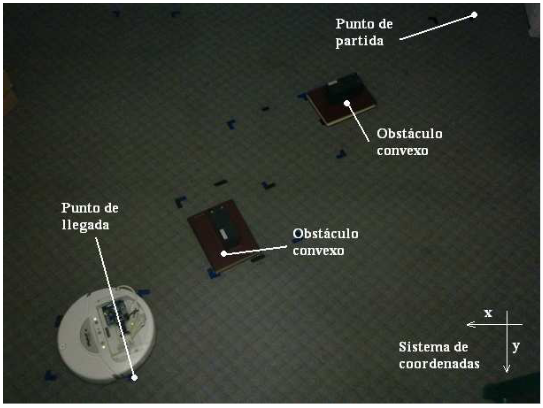
This work presents the implementation of navigation algorithms called worm one and worm two on the iRobot Create mobile robotic platform, which provided the capacity for autonomy to navigate within unknown environments. In addition, radio frequency modules, which operate under the ZigBee standard, were used to provide wireless communication between the robot and a PC. Communication tests were performed to determine the maximum working distance the RF modules can operate indoors. At the same time, for the performance analysis of the primary navigation algorithms mounted on the mobile robotic platform, three scenarios were defined where the robot's certainty of having reached the goal was verified.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms: Authors retain the copyright and guarantee the journal the right to be the first publication of the work, as well as, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others share the work with an acknowledgment of the authorship of the work and the initial publication in this journal. Authors may separately establish additional agreements for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published in the journal (for example, placing it in an institutional repository or publishing it in a book), with acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal. Authors are allowed and encouraged to disseminate their work electronically (for example, in institutional repositories or on their own website) before and during the submission process, as it may lead to productive exchanges as well as further citation earliest and oldest of published works.