Design of a WSN for monitoring CO2 in the air and noise levels in Loja
Main Article Content
Abstract
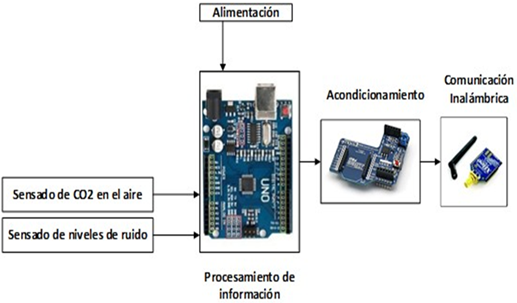
This article describes the design of a wireless network of sensors for monitoring CO2 in the air and noise levels developed for the urban area of the city of Loja. The procedure starts by analyzing the functionality, protocols, and characteristics of the Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) and the implementation of Zigbee communication technology. Then, the monitoring scenario was determined for the network design through the city's more significant concentration of socio-economic activity. From these scenarios, the sectorization of the city center was preceded, establishing the primary sources of CO2 emission and noise levels. Then, the simulation was carried out using the Riverbed Modeler software to determine the evaluation parameters, such as the transmission speed, the delay, and the packets received from the chosen technology. Also, the sensor nodes and the coordinating node were designed to allow the establishment and communication of the network through the XBee PRO S2B module of the Zigbee technology. Finally, to evaluate the designed network, two types of tests were performed: a reception power level test and a validation test of the operation of the network based on the construction and implementation of prototypes of the proposed sensors, a node coordinator, and two sensor nodes (one node for CO2 monitoring and one for noise). The generated information is displayed in a graphical interface developed in the VS Express 2017 software.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms: Authors retain the copyright and guarantee the journal the right to be the first publication of the work, as well as, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others share the work with an acknowledgment of the authorship of the work and the initial publication in this journal. Authors may separately establish additional agreements for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published in the journal (for example, placing it in an institutional repository or publishing it in a book), with acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal. Authors are allowed and encouraged to disseminate their work electronically (for example, in institutional repositories or on their own website) before and during the submission process, as it may lead to productive exchanges as well as further citation earliest and oldest of published works.
How to Cite
References
[2] M. Alfie Cohen and O. Castillo Salinas, "Noise in the city. Acustic pollution and the walkable city," Estudios demográficos y urbanos, vol. 32, 2017.
[3] Comisión Federal para la Protección contra Riesgos, "Efectos a la salud por la contaminación del aire ambientes," 2017. [Online]. Available: https://www.gob.mx/cofepris/acciones-y-programas/3- efectos-a-la-salud-por-la-contaminacion-del-aire- ambiente. [Accessed julio 2019].
[4] Romero, C., Jaimes, J., & González, D., " Parámetros de configuración en módulos XBEE-PRO® S2B ZB para medición de variables ambientales.," Tecnura, vol. 19, no. 45, pp. 141-157, 2015.
[5] Microsoft, "Visual Studio," [Online]. Available: https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/es/vs/. [Accessed Mayo 2019].
[6] C. P. Towsend and S. W. Arms, "Wireless Sensor Networks: Principles and Applications," in Sensor Technology Handbook, 2004, pp. 439-449.
[7] J. P. Iñiguez Armijos, Análisis Espacio - Temporal del ruido ambiental en la ciudad de Loja, Loja: UTPL, 2014.
[8] OMS, "Global ambient air pollution," 2019. [Online]. Available: http://maps.who.int/airpollution/.
[9] UCOT, "Transparencia 2019," 2019. [Online]. Available: https://www.loja.gob.ec/contenido/ucot.
[10] Ó. T. Artero, ARDUINO. Curso práctico de formación, Madrid: RC Libros, 2013.
[11] Ministerio del Ambiente, "Ministerio del Ambiente - Calidad Ambiental," Gobierno de la República del Ecuador, 2019. [Online]. Available: http://www.ambiente.gob.ec/biblioteca/. [Accessed 2019].
[12] I. Akyildiz and M. Vuran, "Wireless Sensor Networks," in Advanced Texts In Communications and Networking, New Jersey, Mankrono Print Media, 2010, pp. 413-502.
[13] R. Faludi, Building Wireless Sensor Networks, New York: BRIAN, 2010, p. 320.
[14] S. Hasan, M. Z. Hussain and R. K. Singh, "A Survey of Wireless Sensor Network.," 2013. [Online]. Available: http://ijetae.com.
[15] Libelium, "Libelium Comunicaciones Distribuidas SL," 2015. [Online]. Available: http://www.libel m.com/resources/top_50_iot_sensor_applications_ranking.
[16] E. J. Guaña Moña, "Protocolos WSN," in Diseño de una red de sensores inalambricos (WSN) para monitorear parámetros realcionados con la agricultura., Escuela Politécnica Nacional, 2016, pp. 25-31.