Statistical evaluation of pseudorandom sequence generators for energy dispersion applications
Main Article Content
Abstract
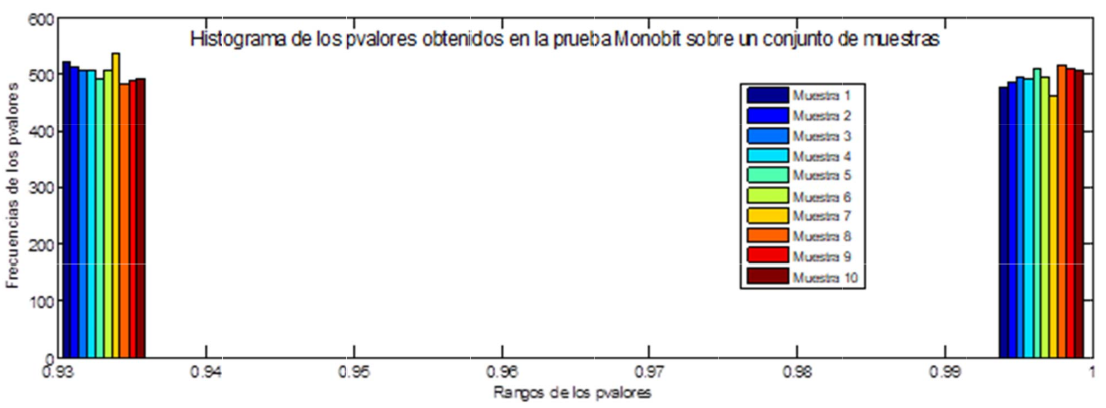
A set of statistical tests is proposed, and with them it is evaluated three pseudorandom number generators PRNGs and two pseudorandom bit sequence generators PRBSs, which could be applied in the process of energy dispersion. With the generators analyzed is reached to the conclusion that none exceeds all statistical tests proposed.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms: Authors retain the copyright and guarantee the journal the right to be the first publication of the work, as well as, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others share the work with an acknowledgment of the authorship of the work and the initial publication in this journal. Authors may separately establish additional agreements for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published in the journal (for example, placing it in an institutional repository or publishing it in a book), with acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal. Authors are allowed and encouraged to disseminate their work electronically (for example, in institutional repositories or on their own website) before and during the submission process, as it may lead to productive exchanges as well as further citation earliest and oldest of published works.
How to Cite
References
[2] ETSI, “Digital Radio Mondiale (DRM). System Specification” Enero 2014. [En línea]. Disponible: http://www.drm.org/wpcontent/uploads/2014/01/DRM-System-Specification-ETSI-ES-201-980-V4.1.1-2014-01.pdf. [Último acceso: 21 Octubre 2014].
[3] Asociación Brasileña de Normas Técnicas, “NBR 15601”, 11 Noviembre 2007. [En línea]. Disponible: http://www.upjet.org.ar/archivos_noticias/356-1.pdf. [Último acceso: 21 Octubre 2014].
[4] Ned, Corron; Billy Reed; Blakely Jonathan; Krishna Myneni; Shawn Pethel; “Chaotic scrambling for Wireless analog video”; Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, vol. 15, Issue 9, pp. 2504-2513, 2010.
[5] Galia, Marinova; Zdravka, Tchobanova; “Simulation, Measurement and Test Environment for Pseudo Random Number Generator Circuits”, Research on Electric and Electronic Measurement for the Economic Upturn, vol. 20, pp. 15-17, 2014.
[6] Goretti, Campo, Echanobe; “Circuitos digitales basados en FPGA para generación de números aleatorios”, [En línea]. Disponible: http://gtts.ehu.es/dEyE/Actualizable/Anual/Curso05-06/VI_Jornadas_IE/trabajos_dirigidos/Goreti_Sevillano.pdf [Último acceso: 27 Octubre 2014].
[7] Raj, Katti; Rajesh, Kavasseri; Vyasa, Sai, “Pseudorandom bit generation using coupled congruential generators”, Transactions on Circuits and Systems II, vol. 57, nº 3, pp. 203-207, 2010.
[8] Xinjia, Chen; Guoxiang, Gu; Kemin, Zhou; “Measurement complexity of Rayleigh Fading Channels”, IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 58, issue: 7, pp. 3776-3781, 2009.
[9] S. Morris y A. Smith-Chaigneau, Interactive TV Standars. A guide to MHP, OCAP and JavaTV., Burlington, USA: Focal Press, 2013, p. 28.
[10] H.-J. Zepernick y A. Finger, Pseudo ramdom signal processing. Theory and applications., Primera ed., Chischester, Inglaterra: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., 2005.
[11] A. Rukhin, J. Soto, J. Nechvatal, M. Smid y E. Barker, “A Statistical Test Suite for Random and Pseudorandom Number Generators for Cryptographic Applications.”, Abril 2010. [En línea]. Disponible: http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/nistpubs/800-22-rev1a/SP800-22rev1a.pdf. [Último acceso: 9 Octubre 2014].